The landscape of equity trading on Wall Street has been shaped by intense competition among the industry’s most prominent investment banks. Over the past six years, three financial giants—Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, and JPMorgan Chase—have consistently dominated the equity trading revenue space, each carving out their unique market position while responding to evolving market conditions, regulatory changes, and unprecedented global events.
The quarterly equity trading revenue data from 2019 through 2025 reveals a fascinating story of resilience, adaptation, and strategic positioning. These three institutions have not only weathered significant market volatility but have also capitalized on opportunities created by changing investor behavior, technological advancement, and shifting market dynamics. Their performance in equity trading serves as a barometer for broader market health and provides insights into the strategic priorities of America’s largest financial institutions.
Understanding the trajectories of these trading revenues offers valuable insights into market cycles, the impact of global events on financial markets, and the competitive dynamics that drive innovation in trading technology and client services. This analysis examines the patterns, trends, and key factors that have influenced equity trading performance across these major players over a transformative period in financial markets.
Market Leadership and Competitive Dynamics

Goldman Sachs: The Consistent Leader
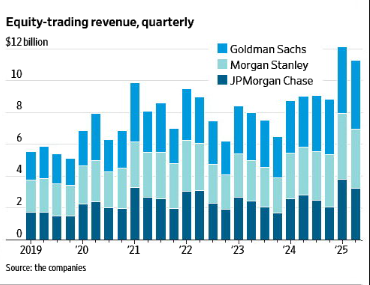
Goldman Sachs has maintained its position as the equity trading revenue leader throughout most of the analyzed period, demonstrating the strength of its institutional client relationships and trading infrastructure. The firm’s revenue consistently reached the highest peaks, particularly notable in the volatile periods of 2020 and 2021, where quarterly revenues approached or exceeded $2.5 billion.
Goldman’s dominance stems from several key factors: its deep institutional client base, sophisticated trading technology, and strong presence in both cash equities and derivatives markets. The firm’s ability to maintain higher revenue levels during both bull and bear markets reflects its diversified trading strategies and robust risk management capabilities. Even during quieter market periods, Goldman typically maintained revenue levels above $1.5 billion quarterly, showcasing the stability of its trading franchise.
The firm’s performance during the COVID-19 pandemic period was particularly impressive, with revenues surging as market volatility created abundant trading opportunities. Goldman’s traders capitalized on increased client activity, wider bid-ask spreads, and heightened demand for market-making services across equity markets.
Morgan Stanley: The Steady Competitor
Morgan Stanley has consistently held the second position in equity trading revenues, typically generating between $1.2 billion and $2.2 billion quarterly. The firm’s steady performance reflects its balanced approach to equity trading, combining institutional client services with a significant wealth management platform that generates consistent equity trading flow.
Morgan Stanley’s equity trading revenue has shown remarkable consistency, with fewer extreme peaks and valleys compared to its competitors. This stability suggests a well-diversified revenue stream that includes both institutional block trading and retail-driven flow from its extensive wealth management business. The firm’s integration of wealth management and institutional trading has created synergies that help maintain steady revenue generation across different market cycles.
The bank’s strategic focus on prime brokerage and equity derivatives has also contributed to its strong market position. Morgan Stanley’s ability to serve both institutional and high-net-worth individual clients provides natural hedging against market downturns that might affect purely institutional-focused competitors.
JPMorgan Chase: The Resilient Third
JPMorgan Chase, while typically ranking third in equity trading revenues, has demonstrated remarkable resilience and growth trajectory. The bank’s revenues have generally ranged from $800 million to $1.8 billion quarterly, with notable strength during periods of market stress and increased volatility.
JPMorgan’s position reflects its role as a universal bank with significant commercial banking relationships that translate into equity trading opportunities. The firm’s corporate client base provides a natural source of equity trading flow through IPOs, secondary offerings, and corporate finance activities. This diversified approach has helped JPMorgan maintain steady performance even when pure trading conditions are challenging.
The bank’s investment in trading technology and electronic market making has also enhanced its competitive position. JPMorgan’s ability to leverage its balance sheet strength during volatile periods has enabled it to capture market share during critical moments when other firms might reduce risk-taking capacity.
Temporal Trends and Market Cycles

The Pre-Pandemic Baseline (2019-Early 2020)
The period from 2019 through early 2020 established a baseline for equity trading revenues that would later be dramatically altered by global events. During this relatively stable period, Goldman Sachs typically generated between $1.8-2.3 billion quarterly, Morgan Stanley ranged from $1.3-1.8 billion, and JPMorgan Chase maintained levels between $900 million and $1.4 billion.
This period was characterized by steady market growth, moderate volatility, and traditional trading patterns. The revenue levels during this time reflected normal market-making spreads, regular institutional trading flows, and typical seasonal patterns. Corporate earnings were generally strong, market valuations were rising steadily, and trading volumes followed predictable patterns around earnings seasons and major economic announcements.
The consistency of revenues during this period also reflected the maturation of electronic trading systems and the establishment of steady competitive positions among the major players. Each firm had found its niche and developed sustainable revenue streams that could weather normal market fluctuations.
The Pandemic Surge (2020-2021)
The COVID-19 pandemic created unprecedented conditions in equity markets, leading to explosive growth in trading revenues for all three firms. The period from Q1 2020 through Q4 2021 saw dramatic increases in equity trading activity, driven by extreme market volatility, massive government stimulus programs, and fundamental shifts in investor behavior.
Goldman Sachs reached peak performance during this period, with several quarters exceeding $2.5 billion in equity trading revenue. The firm’s ability to navigate the extreme volatility of March 2020, when markets fell precipitously before staging a remarkable recovery, demonstrated the value of its trading expertise and client relationships. The subsequent bull market, fueled by low interest rates and fiscal stimulus, created abundant opportunities for equity trading profits.
Morgan Stanley also benefited significantly from the pandemic-era trading boom, with revenues reaching levels above $2 billion in multiple quarters. The firm’s wealth management platform proved particularly valuable during this period, as retail investors became increasingly active in equity markets. The combination of institutional volatility and retail trading activity created ideal conditions for Morgan Stanley’s diversified trading model.
JPMorgan Chase saw perhaps the most dramatic improvement in its relative position during this period, with several quarters approaching or exceeding $1.8 billion in revenue. The bank’s strong balance sheet and market-making capabilities allowed it to capitalize on the increased trading volumes and wider spreads that characterized the volatile pandemic period.
The Normalization Period (2022-2023)
As markets began to normalize following the initial pandemic disruption, equity trading revenues across all three firms showed a gradual decline from peak levels. The period from 2022 through 2023 was marked by concerns about inflation, Federal Reserve policy changes, and geopolitical tensions, creating a different type of market environment than the pandemic-driven volatility.
During this normalization period, revenues generally settled into ranges more comparable to pre-pandemic levels, though often remaining somewhat elevated due to structural changes in market behavior. Goldman Sachs typically maintained revenues between $1.5-2.2 billion, Morgan Stanley ranged from $1.2-1.9 billion, and JPMorgan Chase generally stayed between $1.0-1.6 billion.
This period demonstrated the sustainability of the changes in trading behavior that had emerged during the pandemic. While revenues declined from peak levels, they remained generally higher than the 2019 baseline, suggesting that some of the increased trading activity and market participation had become permanent features of the market landscape.
Strategic Positioning and Competitive Advantages
Technology and Infrastructure Investments
The ability of these three firms to maintain their market-leading positions in equity trading revenue reflects significant investments in trading technology and market infrastructure. Each institution has developed sophisticated electronic trading platforms, algorithmic execution capabilities, and risk management systems that enable them to serve institutional clients effectively while managing their own trading risks.
Goldman Sachs has long been recognized for its trading technology, with systems that can handle high-frequency trading, complex derivatives, and large block transactions. The firm’s investment in artificial intelligence and machine learning has enhanced its ability to predict market movements and optimize trade execution. These technological capabilities have been crucial in maintaining its revenue leadership across different market conditions.
Morgan Stanley’s technology investments have focused on integrating its wealth management and institutional trading platforms, creating seamless connectivity between different client segments. This integration has enabled the firm to capture trading flows from multiple sources and optimize execution across its entire client base. The firm’s emphasis on user experience and client-facing technology has helped maintain strong client relationships.
JPMorgan Chase has leveraged its broader technological infrastructure and substantial investment capacity to build world-class trading systems. The bank’s ability to integrate equity trading with its corporate banking relationships has created unique technological solutions that serve multiple business lines simultaneously. This comprehensive approach has enhanced the bank’s competitive position in equity trading.
Client Relationship Strategies
The sustained success of these three firms in equity trading reflects their ability to build and maintain strong client relationships across different market cycles. Each institution has developed distinct approaches to client service that leverage their unique strengths and market positions.
Goldman Sachs has maintained its reputation as the premier institutional trading partner, with deep relationships among hedge funds, pension funds, and other sophisticated investors. The firm’s research capabilities, market insights, and execution quality have created strong client loyalty that translates into consistent trading revenue. Goldman’s focus on serving the most demanding institutional clients has enabled it to command premium pricing for its services.
Morgan Stanley’s dual approach, serving both institutional clients and high-net-worth individuals through its wealth management platform, has created a more diversified and stable revenue base. The firm’s ability to serve clients across the risk spectrum—from conservative wealth management clients to aggressive hedge funds—has provided natural diversification that smooths revenue volatility.
JPMorgan Chase’s relationship strategy leverages its position as a universal bank, creating equity trading opportunities through its corporate banking relationships. When companies need to raise capital, execute buyback programs, or manage employee stock plans, JPMorgan’s existing relationships often translate into equity trading revenue. This approach has provided the bank with a steady flow of trading opportunities that complement its market-making activities.
Risk Management and Capital Allocation
The ability to generate consistent equity trading revenues while managing risk effectively has been a key differentiator among these institutions. Each firm has developed sophisticated risk management frameworks that enable them to optimize their trading activities while maintaining regulatory compliance and protecting shareholder capital.
Goldman Sachs has historically operated with higher risk tolerance in its trading businesses, enabling it to capture larger profits during favorable market conditions. However, the firm has also invested heavily in risk management systems that can quickly reduce exposure when market conditions deteriorate. This balanced approach has enabled Goldman to maintain its revenue leadership while avoiding catastrophic losses.
Morgan Stanley’s risk management approach reflects its need to balance the interests of trading clients with those of wealth management clients. The firm has developed systems that can manage risk across different business lines while ensuring that trading activities don’t create conflicts with its fiduciary responsibilities to wealth management clients.
JPMorgan Chase benefits from its substantial capital base and diversified business model, which provides natural hedging for its equity trading activities. The bank’s risk management systems are integrated across all business lines, enabling comprehensive risk assessment and capital optimization. This integrated approach has helped JPMorgan maintain steady trading performance even during challenging market conditions.
Future Outlook and Market Evolution
Emerging Market Trends
The equity trading landscape continues to evolve rapidly, driven by technological innovation, changing regulatory requirements, and shifts in investor behavior. The three market leaders must adapt to these changes while maintaining their competitive positions and revenue generation capabilities.
The growth of electronic and algorithmic trading has fundamentally changed market structure, creating both opportunities and challenges for traditional market makers. Firms that can effectively combine human expertise with advanced technology are likely to maintain competitive advantages, while those that fail to innovate may see their market positions erode.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing has become increasingly important, creating new trading flows and opportunities. Firms that can effectively serve clients’ ESG investment needs while providing competitive execution are likely to capture growing market share in this expanding segment.
The rise of retail trading, accelerated during the pandemic, has created new dynamics in equity markets. Firms that can effectively serve both institutional and retail segments may have advantages in capturing diverse trading flows and maintaining revenue stability across different market conditions.
Technological Disruption and Innovation
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly important in equity trading, enabling more sophisticated risk management, better execution algorithms, and enhanced client service. The firms that most effectively integrate these technologies into their trading operations are likely to maintain competitive advantages.
Blockchain technology and digital assets represent potential disruption to traditional equity trading models. While still evolving, these technologies could create new trading opportunities or fundamentally change market structure. Firms that position themselves effectively for these changes may capture significant future revenue opportunities.
Cloud computing and data analytics are enabling new approaches to trade execution and risk management. The ability to process vast amounts of market data in real-time and extract actionable insights has become increasingly important for maintaining competitive positions.
Regulatory Environment and Compliance
The regulatory environment for equity trading continues to evolve, with increased focus on market transparency, client protection, and systemic risk management. Firms that can effectively navigate regulatory requirements while maintaining efficient trading operations will have competitive advantages.
Changes in market structure regulations could significantly impact trading revenues and competitive dynamics. Firms must remain agile in adapting to regulatory changes while maintaining their ability to serve clients effectively.
International regulatory coordination and standardization may create new opportunities for global equity trading while also increasing compliance complexity. Firms with strong regulatory and compliance capabilities are likely to be better positioned for success in this evolving environment.
Conclusion: Sustained Excellence in a Dynamic Market
The equity trading revenue performance of Goldman Sachs, Morgan Stanley, and JPMorgan Chase from 2019 through 2025 demonstrates the resilience and adaptability of these market-leading institutions. Each firm has successfully navigated unprecedented market conditions while maintaining their competitive positions and generating substantial returns for shareholders.
Looking forward, success in equity trading will require continued investment in technology, maintenance of strong client relationships, effective risk management, and the ability to adapt to changing market conditions. The firms that can best balance these requirements while innovating for the future are likely to maintain their leadership positions in this critical business segment.
The evolution of equity trading revenues over this period illustrates both the challenges and opportunities present in modern financial markets. As markets continue to evolve, these institutions must remain focused on delivering value to clients while generating sustainable returns, ensuring their continued prominence in the global equity trading landscape.