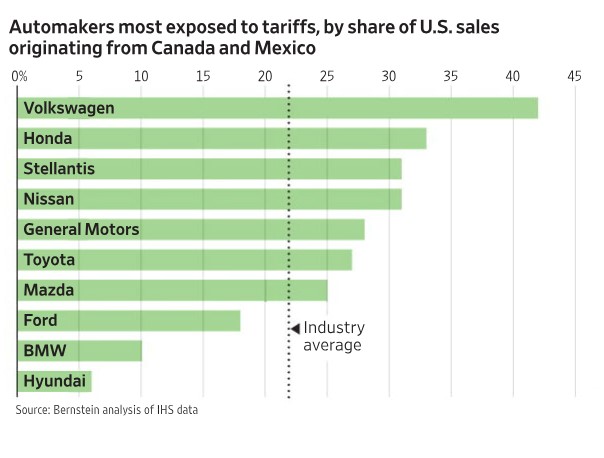
The analysis highlights that Volkswagen has the highest exposure, with nearly 45% of its U.S. sales originating from Canada and Mexico. Other manufacturers, including Honda, Stellantis, Nissan, and General Motors, also have substantial exposure. The industry average sits at around 20%, with some companies falling below this threshold, such as Ford, BMW, and Hyundai.
Volkswagen’s Heavy Dependence on North American Imports
Volkswagen’s high exposure is a result of its production strategy, which relies on manufacturing facilities in Mexico for certain models that are then exported to the U.S. This dependence makes the company particularly vulnerable to tariff fluctuations, affecting its pricing and competitive positioning in the American market.
The Position of Japanese Automakers
Honda, Nissan, Mazda, and Toyota are among the Japanese automakers with significant exposure to tariffs. These companies operate numerous manufacturing plants in Mexico to take advantage of lower production costs while still serving the U.S. market. Any increase in tariffs could lead to costlier imports, affecting affordability and sales volume.
The Role of Stellantis and General Motors
Stellantis, formed from the merger of Fiat Chrysler and PSA Group, has a diversified production base but remains exposed to tariffs due to its reliance on North American production hubs. General Motors, one of the largest U.S. automakers, also depends on Canadian and Mexican imports, making it susceptible to policy changes affecting trade agreements such as the USMCA (United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement).
Industry Average and Automakers with Lower Exposure
Companies like Ford, BMW, and Hyundai have relatively lower exposure compared to their competitors. Ford, for instance, has a strong domestic production presence in the U.S., reducing its reliance on imports. BMW and Hyundai also have significant U.S.-based manufacturing, mitigating the risk of tariff-related cost increases.
Conclusion The exposure of automakers to tariffs on Canadian and Mexican imports varies widely, with Volkswagen, Honda, Stellantis, and Nissan being among the most affected. As trade policies continue to evolve, these companies must navigate the risks and adapt their business strategies accordingly. The future of North American automotive trade will depend on regulatory decisions, economic conditions, and strategic shifts within the industry.